Oak Ridge Quantum Science Center prioritizes joined-up thinking, multidisciplinary impacts
Travis Humble is a research leader who’s thinking big, dreaming bold, yet laser-focused on operational delivery. The long-game? To translate advances in fundamental quantum science into a portfolio of enabling technologies that will fast-track the practical deployment of quantum computers for at-scale scientific, industrial and commercial applications.
As director of the Quantum Science Center (QSC) at Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL) in East Tennessee, Humble and his management team are well placed to transform that research vision into scientific, economic and societal upside. Funded to the tune of $115 million through its initial five-year programme (2020–25), QSC is one of five dedicated National Quantum Information Science Research Centers (NQISRC) within the US Department of Energy (DOE) National Laboratory system.
Validation came in spades last month when, despite the current turbulence around US science funding, QSC was given follow-on DOE backing of $125 million over five years (2025–30) to create “a new scientific ecosystem” for fault-tolerant, quantum-accelerated high-performance computing (QHPC). In short, QSC will target the critical research needed to amplify the impact of quantum computing through its convergence with leadership-class exascale HPC systems.
“Our priority in Phase II QSC is the creation of a common software ecosystem to host the compilers, programming libraries, simulators and debuggers needed to develop hybrid-aware algorithms and applications for QHPC,” explains Humble. Equally important, QSC researchers will develop and integrate new techniques in quantum error correction, fault-tolerant computing protocols and hybrid algorithms that combine leading-edge computing capabilities for pre- and post-processing of quantum programs. “These advances will optimize quantum circuit constructions and accelerate the most challenging computational tasks within scientific simulations,” Humble adds.
Classical computing, quantum opportunity
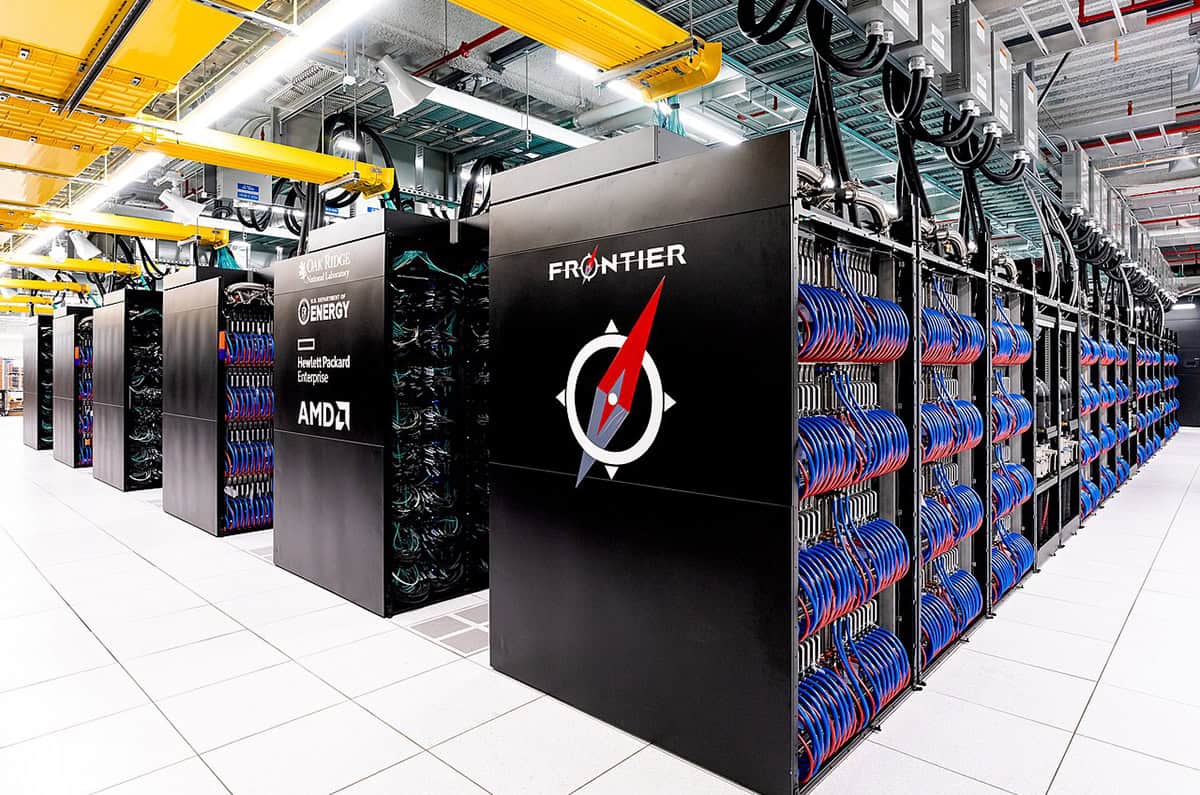
At the heart of the QSC programme sits ORNL’s leading-edge research infrastructure for classical HPC, a capability that includes Frontier, the first supercomputer to break the exascale barrier and still one of the world’s most powerful. On that foundation, QSC is committed to building QHPC architectures that take advantage of both quantum computers and exascale supercomputing to tackle all manner of scientific and industrial problems beyond the reach of today’s HPC systems alone.
“Hybrid classical-quantum computing systems are the future,” says Humble. “With quantum computers connecting both physically and logically to existing HPC systems, we can forge a scalable path to integrate quantum technologies into our scientific infrastructure.”

Industry partnerships are especially important in this regard. Working in collaboration with the likes of IonQ, Infleqtion and QuEra, QSC scientists are translating a range of computationally intensive scientific problems – quantum simulations of exotic matter, for example – onto the vendors’ quantum computing platforms, generating excellent results out the other side.
“With our broad representation of industry partners,” notes Humble, “we will establish a common framework by which scientific end-users, software developers and hardware architects can collaboratively advance these tightly coupled, scalable hybrid computing systems.”
It’s a co-development model that industry values greatly. “Reciprocity is key,” Humble adds. “At QSC, we get to validate that QHPC can address real-world research problems, while our industry partners gather user feedback to inform the ongoing design and optimization of their quantum hardware and software.”
Quantum impact
Innovation being what it is, quantum computing systems will continue to trend on an accelerating trajectory, with more qubits, enhanced fidelity, error correction and fault-tolerance key reference points on the development roadmap. Phase II QSC, for its part, will integrate five parallel research thrusts to advance the viability and uptake of QHPC technologies.
The collaborative software effort, led by ORNL’s Vicente Leyton, will develop openQSE, an adaptive, end-to-end software ecosystem for QHPC systems and applications. Yigit Subasi from Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) will lead the hybrid algorithms thrust, which will design algorithms that combine conventional and quantum methods to solve challenging problems in the simulation of model materials.
Meanwhile, the QHPC architectures thrust, under the guidance of ORNL’s Chris Zimmer, will co-design hybrid computing systems that integrate quantum computers with leading-edge HPC systems. The scientific applications thrust, led by LANL’s Andrew Sornberger, will develop and validate applications of quantum simulation to be implemented on prototype QHPC systems. Finally, ORNL’s Michael McGuire will lead the thrust to establish experimental baselines for quantum materials that ultimately validate QHPC simulations against real-world measurements.
Longer term, ORNL is well placed to scale up the QHPC model. After all, the laboratory is credited with pioneering the hybrid supercomputing model that uses graphics processing units in addition to conventional central processing units (including the launch in 2012 of Titan, the first supercomputer of this type operating at over 10 petaFLOPS).
“The priority for all the QSC partners,” notes Humble, “is to transition from this still-speculative research phase in quantum computing, while orchestrating the inevitable convergence between quantum technology, existing HPC capabilities and evolving scientific workflows.”
Collaborate, coordinate, communicate
Much like its NQISRC counterparts (which have also been allocated further DOE funding through 2030), QSC provides the “operational umbrella” for a broad-scope collaboration of more than 300 scientists and engineers from 20 partner institutions. With its own distinct set of research priorities, that collective activity cuts across other National Laboratories (Los Alamos and Pacific Northwest), universities (among them Berkeley, Cornell and Purdue) and businesses (including IBM and IQM) to chart an ambitious R&D pathway addressing quantum-state (qubit) resilience, controllability and, ultimately, the scalability of quantum technologies.
“QSC is a multidisciplinary melting pot,” explains Humble, “and I would say, alongside all our scientific and engineering talent, it’s the pooled user facilities that we are able to exploit here at Oak Ridge and across our network of partners that gives us our ‘grand capability’ in quantum science [see box, “Unique user facilities unlock QSC opportunities”]. Certainly, when you have a common research infrastructure, orchestrated as part a unified initiative like QSC, then you can deliver powerful science that translates into real-world impacts.”
Unique user facilities unlock QSC opportunities
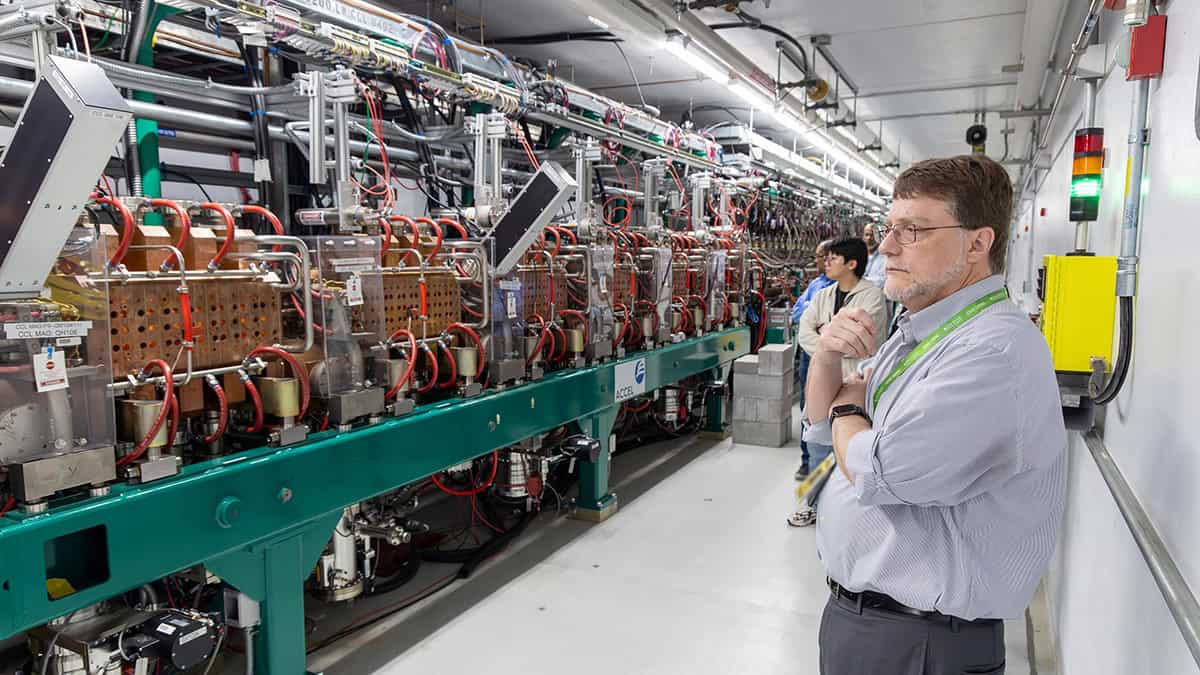

Deconstructed, QSC’s Phase I remit (2020–25) spanned three dovetailing and cross-disciplinary research pathways: discovery and development of advanced materials for topological quantum computing (in which quantum information is stored in a stable topological state – or phase – of a physical system rather than the properties of individual particles or atoms); development of next-generation quantum sensors (to characterize topological states and support the search for dark matter); as well as quantum algorithms and simulations (for studies in fundamental physics and quantum chemistry).
Underpinning that collective effort: ORNL’s unique array of scientific user facilities. A case in point is the Spallation Neutron Source (SNS), an accelerator-based neutron-scattering facility that enables a diverse programme of pure and applied research in the physical sciences, life sciences and engineering. QSC scientists, for example, are using SNS to investigate entirely new classes of strongly correlated materials that demonstrate topological order and quantum entanglement – properties that show great promise for quantum computing and quantum metrology applications.
“The high-brightness neutrons at SNS give us access to this remarkable capability for materials characterization,” says Humble. “Using the SNS neutron beams, we can probe exotic materials, recover the neutrons that scatter off of them and, from the resultant signals, infer whether or not the materials exhibit quantum properties such as entanglement.”
While SNS may be ORNL’s “big-ticket” user facility, the laboratory is also home to another high-end resource for quantum studies: the Center for Nanophase Material Science (CNMS), one of the DOE’s five national Nanoscience Research Centers, which offers QSC scientists access to specialist expertise and equipment for nanomaterials synthesis; materials and device characterization; as well as theory, modelling and simulation in nanoscale science and technology.
Thanks to these co-located capabilities, QSC scientists pioneered another intriguing line of enquiry – one that will now be taken forward elsewhere within ORNL – by harnessing so-called quantum spin liquids, in which electron spins can become entangled with each other to demonstrate correlations over very large distances (relative to the size of individual atoms).
In this way, it is possible to take materials that have been certified as quantum-entangled and use them to design new types of quantum devices with unique geometries – as well as connections to electrodes and other types of control systems – to unlock novel physics and exotic quantum behaviours. The long-term goal? Translation of quantum spin liquids into a novel qubit technology to store and process quantum information.
SNS, CNMS and Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility (OLCF) are DOE Office of Science user facilities.
When he’s not overseeing the technical direction of QSC, Humble is acutely attuned to the need for sustained and accessible messaging. The priority? To connect researchers across the collaboration – physicists, chemists, material scientists, quantum information scientists and engineers – as well as key external stakeholders within the DOE, government and industry.
“In my experience,” he concludes, ”the ability of the QSC teams to communicate efficiently – to understand each other’s concepts and reasoning and to translate back and forth across disciplinary boundaries – remains fundamental to the success of our scientific endeavours.”
Further information
Listen to the Physics World podcast: Oak Ridge’s Quantum Science Center takes a multidisciplinary approach to developing quantum materials and technologies
Scaling the talent pipeline in quantum science
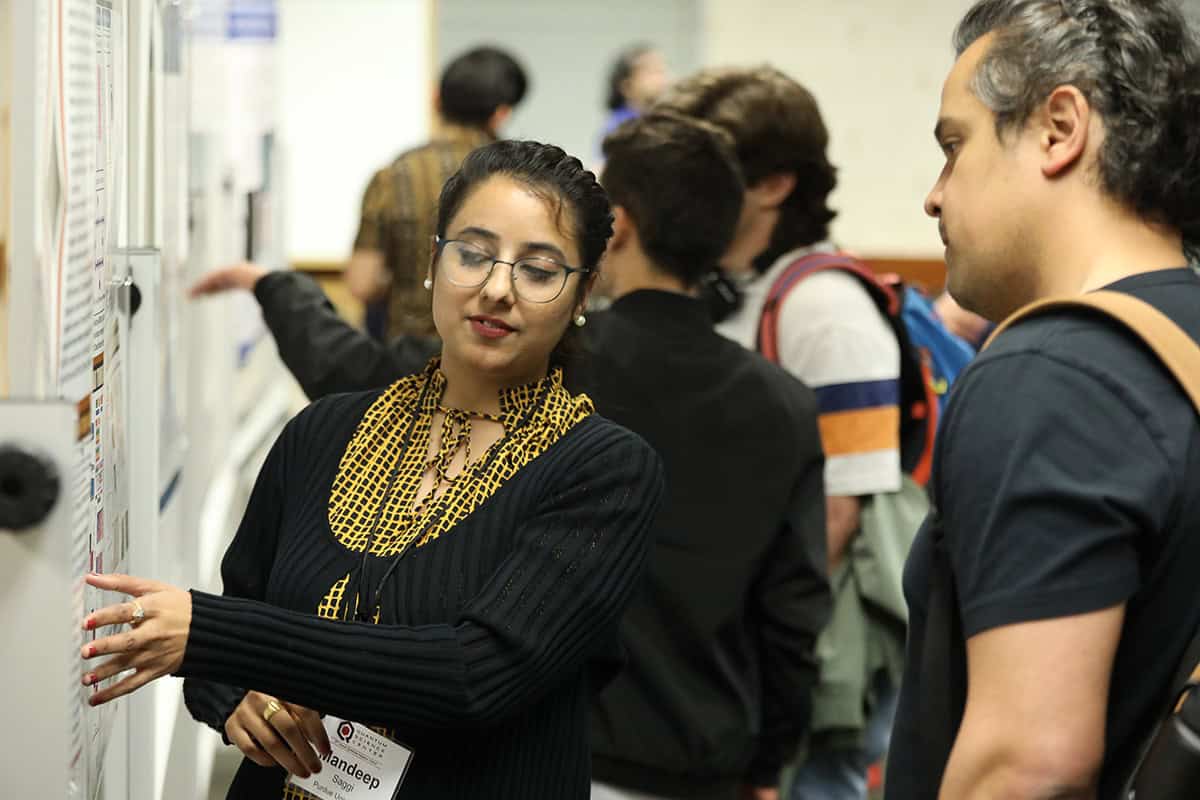

With an acknowledged shortage of skilled workers across the quantum supply chain, QSC is doing its bit to bolster the scientific and industrial workforce. Front-and-centre: the fifth annual QSC Summer School, which was held at Purdue University in April this year, hosting 130 graduate students (the largest cohort to date) through an intensive four-day training programme.
The Summer School sits as part of a long-term QSC initiative to equip ambitious individuals with the specialist domain knowledge and skills needed to thrive in a quantum sector brimming with opportunity – whether that’s in scientific research or out in industry with hardware companies, software companies or, ultimately, the end-users of quantum technologies in key verticals like pharmaceuticals, finance and healthcare.
“While PhD students and postdocs are integral to the QSC research effort, the Summer School exposes them to the fundamental ideas of quantum science elaborated by leading experts in the field,” notes Vivien Zapf, a condensed-matter physicist at Los Alamos National Laboratory who heads up QSC’s advanced characterization efforts.
“It’s all about encouraging the collective conversation,” she adds, “with lots of opportunities for questions and knowledge exchange. Overall, our emphasis is very much on training up scientists and engineers to work across the diversity of disciplines needed to translate quantum technologies out of the lab into practical applications.”
The programme isn’t for the faint-hearted, though. Student delegates kicked off this year’s proceedings with a half-day of introductory presentations on quantum materials, devices and algorithms. Next up: three and a half days of intensive lectures, panel discussions and poster sessions covering everything from entangled quantum networks to quantum simulations of superconducting qubits.
Many of the Summer School’s sessions were also made available virtually on Purdue’s Quantum Coffeehouse Live Stream on YouTube – the streamed content reaching quantum learners across the US and further afield. Lecturers were drawn from the US National Laboratories, leading universities (such as Harvard and Northwestern) and the quantum technology sector (including experts from IBM, PsiQuantum, NVIDIA and JPMorganChase).
The post Oak Ridge Quantum Science Center prioritizes joined-up thinking, multidisciplinary impacts appeared first on Physics World.