Asteroid 2024 YR4’s Possible 2032 Moon Impact — What the Aftermath Could Look Like









Blue Origin announced Jan. 30 that it will halt flights of its New Shepard suborbital vehicle for at least two years as it shifts its focus to human lunar exploration.
The post Blue Origin halts New Shepard flights appeared first on SpaceNews.

NASA is delaying a key fueling test for the Artemis 2 mission because of weather, reducing the chances the launch can take place during its February window.
The post Weather delays Artemis 2 wet dress rehearsal appeared first on SpaceNews.

In this episode of Space Minds, SpaceNews senior staff writer Sandra Erwin sits down with Gen. Shawn Bratton, vice chair of space operations for the U.S. Space Force for a […]
The post A fireside chat with Space Force Gen. Shawn Bratton appeared first on SpaceNews.





Apolink has partnered with ground segment provider RBC Signals to resell the startup’s proposed in-orbit relay services, aiming to fill connectivity gaps when satellites are out of view of terrestrial command-and-control links.
The post RBC Signals partners with in-orbit relay developer Apolink appeared first on SpaceNews.

When I had two kids going through daycare, or nursery as we call it in the UK, every day seemed like a constant fight with germs and illness. After all, at such a young age kids still have a developing immune system and are not exactly hot on personal hygiene.
That same dilemma faced mathematician Lauren Smith from the University of Auckland. She has two children at a “wonderful daycare centre” who often fall ill. As many parents juggling work and parenting will understand, Smith is frequently faced with the issue of whether her kids are well enough to attend daycare.
Smith then thought about how an unethical daycare centre might take advantage of this to maximize its profits – under the assumption that if there are not enough children attending (who still pay) then staff get sent home without pay, and also don’t get sick pay themselves.
“It occurred to me that a sick kid attending daycare could actually be financially beneficial to the centre, while clearly being a detriment to the wellbeing of the other children as well as the staff and the broader community,” Smith told Physics World.
For a hypothetical daycare centre that is solely focused on making as much money as possible, Smith realized that full attendance of sick children is not optimal financially as this requires maximal staffing at all times, whereas zero attendance of sick children does not give an opportunity for the disease to spread such that other children are then sent home.
But in between these two extremes, Smith thought there should be an optimal attendance rate so that the disease is still able to spread and some children – and staff – are sent home. “As a mathematician I knew I had the tools to find it,” adds Smith.
Using the so-called Susceptible-Infected-Recovered model for 100 children, a teacher to child ratio of 1:6 and a recovery rate from illness of 10 days, Smith found that the more infectious the disease, the lower the optimal attendance rate for sick children is, and so the more savings the unethical daycare centre can make.
In other words, the more infectious a disease, fewer ill children are required to attend to spread it around, and so can keep more of them – and importantly staff – at home while still making sure it still spreads to non-infected kids.
For a measles outbreak with a basic reproductive number of 12-18, for example, the model resulted in a potential staff saving of 90 working days, whereas for seasonal flu with a basic reproductive rate of 1.2 to 1.3, the potential staff savings is 4.4 days.
Smith writes in the paper that the work is “not intended as a recipe for unethical daycare centre” but is rather to illustrate the financial incentive that exists for daycare centres to propagate diseases among children, which would lead to more infections of at-risk populations in the wider community.
“I hope that as well as being an interesting topic, it can show that mathematics itself is interesting and is useful for describing the real world,” adds Smith.
The post The physics of an unethical daycare model that uses illness to maximize profits appeared first on Physics World.
When the Titanic was built, her owners famously described her as “unsinkable”. A few days into her maiden voyage, an iceberg in the North Atlantic famously proved them wrong. But what if we could make ships that really are unsinkable? And what if we could predict exactly how long a hazardous iceberg will last before it melts?
These are the premises of two separate papers published independently this week by Chunlei Guo and colleagues at the University of Rochester, and by Daisuke Noto and Hugo N Ulloa of the University of Pennsylvania, both in the US. The Rochester group’s paper, which appears in Advanced Functional Materials, describes how applying a superhydrophobic coating to an open-ended metallic tube can make it literally unsinkable – a claim supported by extensive tests in a water tank. Noto and Ulloa’s research, which they describe in Science Advances, likewise involved a water tank. Theirs, however, was equipped with cameras, lasers and thermochromic liquid crystals that enabled them to track a freely floating miniature iceberg as it melted.
Each study is surprising in its own way. For the iceberg paper, arguably the biggest surprise is that no-one had ever done such experiments before. After all, water and ice are readily available. Fancy tanks, lasers, cameras and temperature-sensitive crystals are less so, yet surely someone, somewhere, must have stuck some ice in a tank and monitored what happened to it?
Noto and Ulloa’s answer is, in effect, no. “Despite the relevance of melting of floating ice in calm and energetic environments…most experimental and numerical efforts to examine this process, even to date, have either fixed or tightly constrained the position and posture of ice,” they write. “Consequently, the relationships between ice dissolution rate and background fluid flow conditions inferred from these studies are meaningful only when a one-way interaction, from the liquid to the solid phase, dominates the melting dynamics.”
The problem, they continue, is that eliminating these approximations “introduces a significant technical challenge for both laboratory experiments and numerical simulations” thanks to a slew of interactions that would otherwise get swept under the rug. These interactions, in turn, lead to complex dynamics such as drifting, spinning and even flipping that must be incorporated into the model. Consequently, they write, “fundamental questions persist: ‘How long does an ice body last?’”
To answer this question, Noto and Ulloa used their water-tank observations (see video) to develop a model that incorporates the thermodynamics of ice melting and mass balance conservation. Based on this model, they correctly predict both the melting rate and the lifespan of freely floating ice under self-driven convective flows that arise from interactions between the ice and the calm, fresh water surrounding it. Though the behaviour of ice in tempestuous salty seas is, they write, “beyond our scope”, their model nevertheless provides a useful upper bound on iceberg longevity, with applications for climate modelling as well as (presumably) shipping forecasts for otherwise-doomed ocean liners.
In the unsinkable tube study, the big surprise is that a metal tube, divided in the middle but open at both ends, can continue to float after being submerged, corroded with salt, tossed about on a turbulent sea and peppered with holes. How is that even possible?
“The inside of the tube is superhydrophobic, so water can’t enter and wet the walls,” Guo explains. “As a result, air remains trapped inside, providing buoyancy.”
Importantly, this buoyancy persists even if the tube is damaged. “When the tube is punctured, you can think of it as becoming two, three, or more smaller sections,” Guo tells Physics World. “Each section will work in the same way of preventing water from entering inside, so no matter how many holes you punch into it, the tube will remain afloat.”
So, is there anything that could make these superhydrophobic structures sink? “I can’t think of any realistic real-world challenges more severe than what we have put them through experimentally,” he says.
We aren’t in unsinkable ship territory yet: the largest structure in the Rochester study was a decidedly un-Titanic-like raft a few centimetres across. But Guo doesn’t discount the possibility. He points out that tubes are made from ordinary aluminium, with a simple fabrication process. “If suitable applications call for it, I believe [human-scale versions] could become a reality within a decade,” he concludes.
The post Saving the <em>Titanic</em>: the science of icebergs and unsinkable ships appeared first on Physics World.

The EU Space Act was formally proposed by the European Commission (EC) on June 25, 2025. While it doesn’t aim to codify all European Union (EU) space activities, it does address several key issues that EU officials have determined are increasingly important to the continent’s concerns: safety, through tracking space objects and mitigating space debris; resilience, […]
The post Making the unprecedented EU Space Act effective for all appeared first on SpaceNews.

A Rocket Lab Electron launched a South Korean imaging satellite Jan. 29 on the rocket’s second flight of the year.
The post Rocket Lab launches South Korean satellite appeared first on SpaceNews.

Plastic has become a global pollutant concern over the last couple of decades: it is widespread in society, not often disposed of effectively, and generates both microplastics (1 µm to 5 mm in size) and nanoplastics (smaller than 1 µm) that have infiltrated many ecosystems – including being found inside humans and animals.
Over time, bulk plastics break down into micro- and nanoplastics through fragmentation mechanisms that create much smaller particles with a range of shapes and sizes. Their small size has become a problem because they are increasingly finding their way into waterways that pollute the environment, into cities and other urban environments, and are now even being transported to remote polar and high-altitude regions.
This poses potential health risks around the world. While the behaviour of micro- and nanoplastics in the atmosphere is poorly understood, it’s thought that they are transported by transcontinental and transoceanic winds, which causes the spread of plastic in the global carbon cycle.
However, the lack of data on the emission, distribution and deposition of atmospheric micro- and nanoplastic particles makes it difficult to definitively say how they are transported around the world. It is also challenging to quantify their behaviour, because plastic particles can have a range of densities, sizes and shapes that undergo physical changes in clouds, all of which affect how they travel.
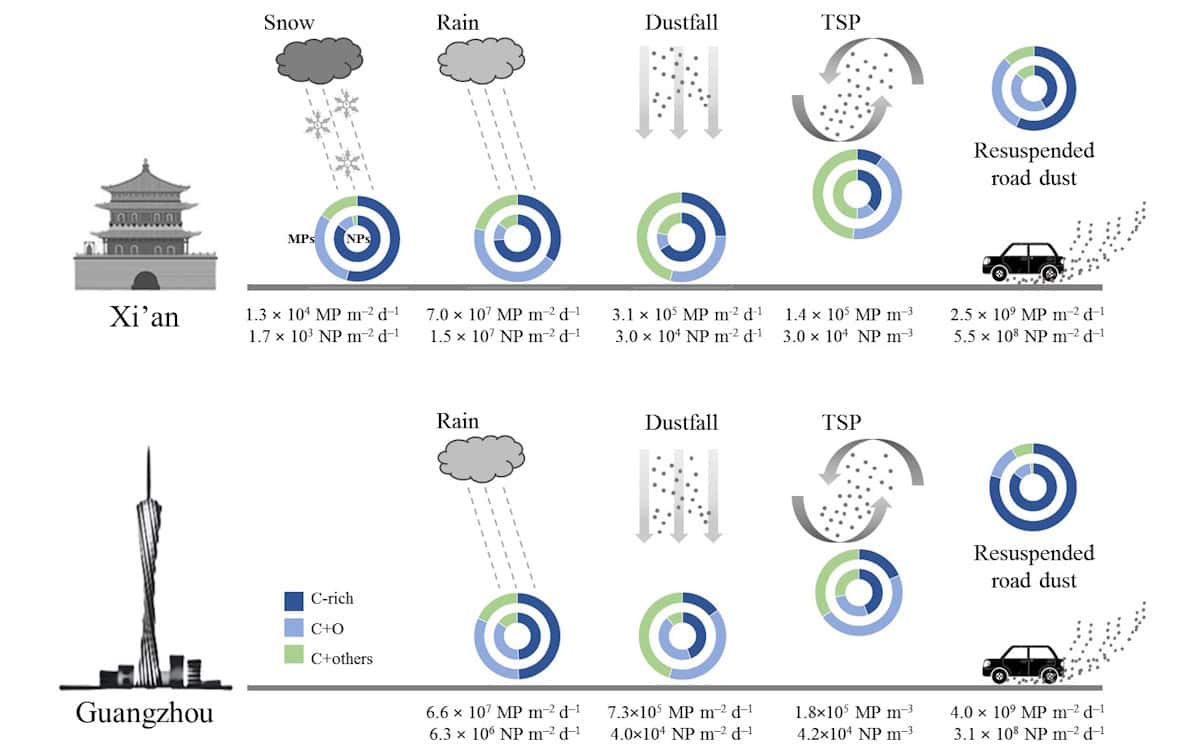
A global team of researchers has developed a new semi-automated microanalytical method that can quantify atmospheric plastic particles present in air dustfall, rain, snow and dust resuspension. The research was performed across two Chinese megacities, Guangzhou and Xi’an.
“As atmospheric scientists, we noticed that microplastics in the atmosphere have been the least reported among all environmental compartments in the Earth system due to limitations in detection methods, because atmospheric particles are smaller and more complex to analyse,” explains Yu Huang, from the Institute of Earth Environment of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IEECAS) and one of the paper’s lead authors. “We therefore set out to develop a reliable detection technique to determine whether microplastics are present in the atmosphere, and if so, in what quantities.”
For this new approach, the researchers employed a computer-controlled scanning electron microscopy (CCSEM) system equipped with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy to reduce human bias in the measurements (which is an issue in manual inspections). They located and measured individual micro- and nanoplastic particles – enabling their concentration and physicochemical characteristics to be determined – in aerosols, dry and wet depositions, and resuspended road dust.
“We believe the key contribution of this work lies in the development of a semi‑automated method that identifies the atmosphere as a significant reservoir of microplastics. By avoiding the human bias inherent in visual inspection, our approach provides robust quantitative data,” says Huang. “Importantly, we found that these microplastics often coexist with other atmospheric particles, such as mineral dust and soot – a mixing state that could enhance their potential impacts on climate and the environment.”
The method could detect and quantify plastic particles as small as 200 nm, and revealed airborne concentrations of 1.8 × 105 microplastics/m3 and 4.2 × 104 nanoplastics/m3 in Guangzhou and 1.4 × 105 microplastics/m3 and 3.0 × 104 nanoplastics/m3 in Xi’an. This is two to six orders of magnitude higher for both microplastic and nanoplastic fluxes than reported previously via visual methods.
The team also found that the deposition samples were more heterogeneously mixed with other particle types (such as dust and other pollution particles) than aerosols and resuspension samples, which showed that particles tend to aggregate in the atmosphere before being removed during atmospheric transport.
The study revealed transport insights that could be beneficial for investigating the climate, ecosystem and human health impacts of plastic particles at all levels. The researchers are now advancing their method in two key directions.
“First, we are refining sampling and CCSEM‑based analytical strategies to detect mixed states between microplastics and biological or water‑soluble components, which remain invisible with current techniques. Understanding these interactions is essential for accurately assessing microplastics’ climate and health effects,” Huang tells Physics World. “Second, we are integrating CCSEM with Raman analysis to not only quantify abundance but also identify polymer types. This dual approach will generate vital evidence to support environmental policy decisions.”
The research was published in Science Advances.
The post Scientists quantify behaviour of micro- and nanoplastics in city environments appeared first on Physics World.


Maj. Gen. Terry Grisham will oversee the move from Colorado Springs to Redstone Arsenal.
The post Alabama National Guard general to manage Space Command headquarters transition appeared first on SpaceNews.





NASA is at a “crossroads” in deciding how to handle logistics for the lunar Gateway as it considers alternative approaches.
The post NASA considering alternatives for Gateway logistics appeared first on SpaceNews.

The Denver-based satellite manufacturer raises $629 million, aims to expand output amid rising U.S. defense budgets
The post York Space goes public, riding Pentagon demand appeared first on SpaceNews.