As with people, age in cosmology does not always extrapolate. An early-career politician may be more likely to win a debate with a student than with a seasoned diplomat, but put all three in a room with a toddler and the toddler will almost certainly get their own way – they are following a different set of rules. A team of global collaborators noticed a similar phenomenon when peering at a cluster of developing galaxies from a time when the universe was just a tenth of its current age.
Cosmological theories suggest that such infant clusters should host much cooler and less abundant gas than more mature clusters. But what the researchers saw was at least five times hotter than expected – apparently not abiding by those rules.
“That’s a massive surprise and forces us to rethink how large structures actually form and evolve in the universe,” says first author Dazhi Zhou, a PhD candidate at the University of British Columbia.
Eyes on the past
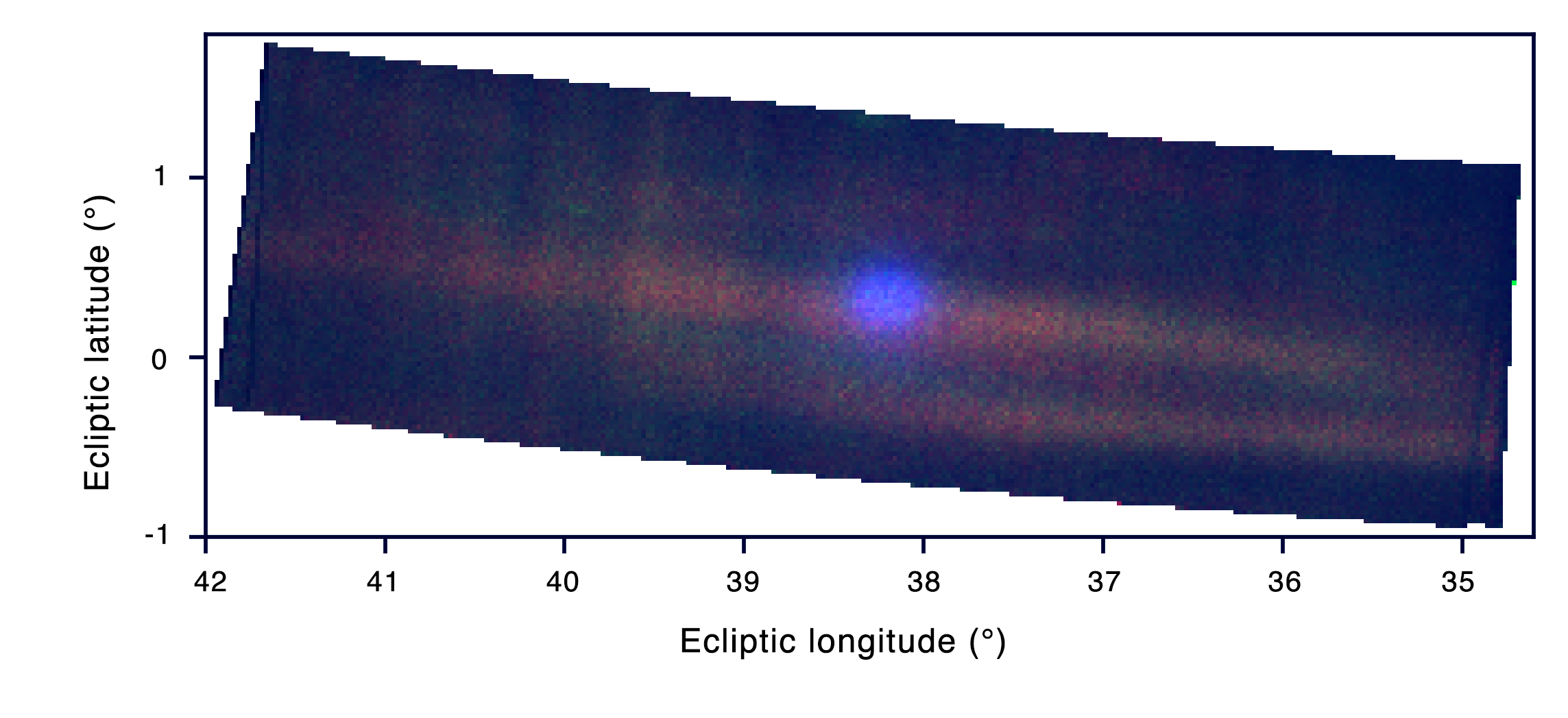
Looking into distant outer space allows us to peer into the past. The protocluster of developing galaxies that Zhou and collaborators investigated – known as SPT2349–56 – is 12.4 billion light years away, so the light observed from it left home when the universe was just 1.4 billion years old. Light from so far away will be quite faint and hard to detect by the time it reaches us, so the researchers used the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) to study SPT2349–56 using a special type of shadow.
As this type of protocluster develops, Zhou explains, the gas around its galaxies becomes so hot that electrons in the gas interact with, and confer some of their energy upon, passing photons. This leaves light passing through the gas with more photons at the higher energy end of the spectrum and fewer at the lower end. When viewing the cosmic microwave background radiation – the “afterglow” left behind by the Big Bang – this results in a shadow at low energies. This energy shift, discovered by physicists Rashid Sunyaev and Yakov Zeldovich, not only reveals the presence of the protocluster, but the strength of this signature indicates the thermal energy of the gas in the protocluster.
The team’s observations were not easy. “This shadow is actually pretty tiny,” Zhou explains. In addition, there is thermal emission from the dust inside galaxies at radio wavelengths, originally estimated to be 20 times stronger than the Sunyaev–Zeldovich signature. “It really is like finding a needle in a haystack,” he adds. Nonetheless, the team did identify a definite Sunyaev–Zeldovich signature from SPT2349–56, with a thermal energy indicating that it was at least five times hotter than expected – thousands of times hotter than the surface of our Sun.
Time to upgrade?
SPT2349–56 has some quirks that may explain its high thermal energy, including three supermassive black holes shooting out jets of high-energy matter – a known but rare phenomenon for these supermassive black holes. However, simulations that take these outbursts into account as a heating mechanism that’s more efficient and occurs much earlier than heating from gravitational collapse (as current models suggest) still do not give the high temperatures observed, perhaps pointing to gaps in our knowledge of the underlying physics.
Eiichiro Komatsu from the Max-Planck-Institut für Astrophysik describes the work as “a wonderful measurement”. Although not directly involved in this research, Komatsu has also looked at what the Sunyaev–Zeldovich effect can reveal about the cosmos. “The amount of thermal energy measured by the authors is staggering, yet its origin is a mystery,” he tells Physics World. He suggests these results will motivate further observations of other systems in the early universe.
“We need to be cautious rather than making any big claim,” adds Zhou. This is the first Sunyaev–Zeldovich detection of a protocluster from the first three billion years of the universe’s existence. Next, he aims to study similar protoclusters, and he hopes others will also work to corroborate the observations.
The research is reported in Nature.
The post Hot ancient galaxy cluster challenges current cosmological models appeared first on Physics World.