PLANCKS physics quiz – the solutions
Question 1: 4D Sun
Imagine you have been transported to another universe with four spatial dimensions. What would the colour of the Sun be in this four-dimensional universe? You may assume that the surface temperature of the Sun is the same as in our universe and is approximately T = 6 × 103 K. [10 marks]
Boltzmann constant, kB = 1.38 × 10−23 J K−1
Speed of light, c = 3 × 108 m s−1
Solution
Black body radiation, spectral density: ε (ν) dν = hνρ (ν) n (ν)
The photon energy, E = hν where h is Planck’s constant and ν is the photon frequency.
The density of states, ρ (ν) = Aνn−1 where A is a constant independent of the frequency and the frequency term is the scaling of surface area of an n-dimensional sphere.
The Bose–Einstein distribution,
n(v)
where k is the Boltzmann constant and T is the temperature.
We let
and get
ε(x)
We do not need the constant of proportionality (which is not simple to calculate in 4D) to find the maximum of ε (x). Working out the constant just tells us how tall the peak is, but we are interested in where the peak is, not the total radiation.
We set this equal to zero for the maximum of the distribution,
This yields x = n (1 − e−x) where
and we can relate
and c being the speed of light.
This equation has the solution x = n +W (−ne−n) where W is the Lambert W function z = W (y) that solves zez = y (although there is a subtlety about which branch of the function). This is kind of useless to do anything with, though. One can numerically solve this equation using bisection/Newton–Raphson/iteration. Alternatively, one could notice that as the number of dimensions increases, e−x is small, so to leading approximation x ≈ n. One can do a little better iterating this, x ≈ n − ne−n which is what we will use. Note the second iteration yields
| Number of dimensions, n | Numerical solution | Approximation |
| 2 | 1.594 | 1.729 |
| 3 | 2.821 | 2.851 |
| 4 (the one we want) | 3.921 | 3.927 |
| 5 | 4.965 | 4.966 |
| 6 | 5.985 | 5.985 |
Using the result above,
616 nm is middle of the spectrum, so it will look white with a green-blue tint. Note, we have used T = 6000 K for the temperature here, as given in the question.
It would also be valid to look at ε (λ) dλ instead of ε (ν) dν.
Question 2: Heavy stuff
In a parallel universe, two point masses, each of 1 kg, start at rest a distance of 1 m apart. The only force on them is their mutual gravitational attraction, F = –Gm1m2/r2. If it takes 26 hours and 42 minutes for the two masses to meet in the middle, calculate the value of the gravitational constant G in this universe. [10 marks]
Solution
First we will set up the equations of motion for our system. We will set one mass to be at position −x and the other to be at x, so the masses are at a distance of 2x from each other. Starting from Newton’s law of gravity:
we can then use Newton’s second law to rewrite the LHS,
which we can simplify to
It is important that you get the right factor here depending on your choice for the particle coordinates at the start. Note there are other methods of getting this point, e.g. reduced mass.
We can now solve the second order ODE above. We will not show the whole process here but present the starting point and key results. We can write the acceleration in terms of the velocity. The initial velocity is zero and the initial position
So,
and once the integrals are solved we can rearrange for the velocity,
Now we can form an expression for the total time taken for the masses to meet in the middle,
There are quite a few steps involved in solving this integral, for these solutions, we shall make use of the following (but do attempt to solve it for yourselves in full).
Hence,
We can now rearrange for G and substitute in the values given in the question, don’t forget to convert the time into seconds.
This is the generally accepted value for the gravitational constant of our universe as well.
Question 3: Just like clockwork
Consider a pendulum clock that is accurate on the Earth’s surface. Figure 1 shows a simplified view of this mechanism.
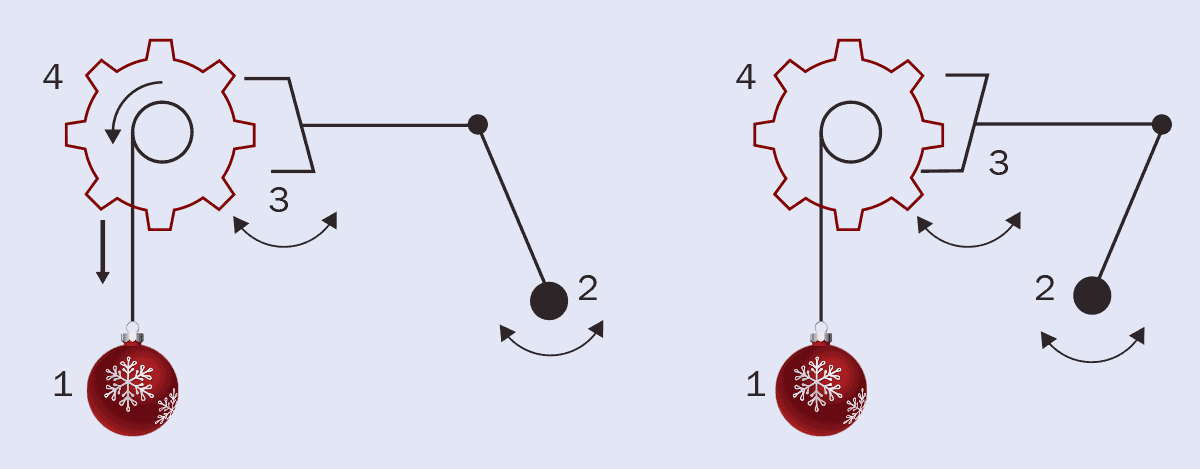
A pendulum clock runs on the gravitational potential energy from a hanging mass (1). The other components of the clock mechanism regulate the speed at which the mass falls so that it releases its gravitational potential energy over the course of a day. This is achieved using a swinging pendulum of length l (2), whose period is given by
where g is the acceleration due to gravity.
Each time the pendulum swings, it rocks a mechanism called an “escapement” (3). When the escapement moves, the gear attached to the mass (4) is released. The mass falls freely until the pendulum swings back and the escapement catches the gear again. The motion of the falling mass transfers energy to the escapement, which gives a “kick” to the pendulum that keeps it moving throughout the day.
Radius of the Earth, R = 6.3781 × 106 m
Period of one Earth day, τ0 = 8.64 × 104 s
How slow will the clock be over the course of a day if it is lifted to the hundredth floor of a skyscraper? Assume the height of each storey is 3 m. [4 marks]
Solution
We will write the period of oscillation of the pendulum at the surface of the Earth to be
.
At a height h above the surface of the Earth the period of oscillation will be
,
where g0 and gh are the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the Earth and a height h above it respectively.
We can define τ0 to be the total duration of the day which is 8.64 × 104 seconds and equal to N complete oscillations of the pendulum at the surface. The lag is then τh which will equal N times the difference in one period of the two clocks, τh = NΔT, where ΔT = (Th − T0). We can now take a ratio of the lag over the day and the total duration of the day:
Then by substituting in the expressions we have for the period of a pendulum at the surface and height h we can write this in terms of the gravitational constant,
[Award 1 mark for finding the ratio of the lag over the day and the total period of the day.]
The acceleration due to gravity at the Earth’s surface is
where G is the universal gravitational constant, M is the mass of the Earth and R is the radius of the Earth. At an altitude h, it will be
[Award 1 mark for finding the expression for the acceleration due to gravity at height h.]
Substituting into our expression for the lag, we get:
This simplifies to an expression for the lag over a day. We can then substitute in the given values to find,
[Award 2 marks for completing the simplification of the ratio and finding the lag to be ≈ 4 s.]
Question 4: Quantum stick
Imagine an infinitely thin stick of length 1 m and mass 1 kg that is balanced on its end. Classically this is an unstable equilibrium, although the stick will stay there forever if it is perfectly balanced. However, in quantum mechanics there is no such thing as perfectly balanced due to the uncertainty principle – you cannot have the stick perfectly upright and not moving at the same time. One could argue that the quantum mechanical effects of the uncertainty principle on the system are overpowered by others, such as air molecules and photons hitting it or the thermal excitation of the stick. Therefore, to investigate we would need ideal conditions such as a dark vacuum, and cooling to a few millikelvins, so the stick is in its ground state.
Moment of inertia for a rod,
where m is the mass and l is the length.
Uncertainty principle,
There are several possible approximations and simplifications you could make in solving this problem, including:
sinθ ≈ θ for small θ
and
Calculate the maximum time it would take such a stick to fall over and hit the ground if it is placed in a state compatible with the uncertainty principle. Assume that you are on the Earth’s surface. [10 marks]
Hint: Consider the two possible initial conditions that arise from the uncertainty principle.
Solution
We can imagine this as an inverted pendulum, with gravity acting from the centre of mass and at an angle θ from the unstable equilibrium point.
[Award 1 mark for a suitable diagram of the system.]
We must now find the equations of motion of the system. For this we can use Newton’s second law in its rotational form τ = Iα (torque = moment of inertia × angular acceleration). We have another equation for torque we can use as well
where r is the distance from the pivot to the centre of mass and F is the force, which in this case is gravity mg. We can then equate these giving
Substituting in the given moment of inertia of the stick and that the angular acceleration
We can cancel a few things and rearrange to get a differential equation of the form:
we then can take the small angle approximation sin θ ≈ θ, resulting in
[Award 2 marks for finding the equation of motion for the system and using the small angle approximation.]
Solve with ansatz of θ = Aeωt + Be−ωt, where we have chosen
We can clearly see that this will satisfy the differential equation
Now we can apply initial conditions to find A and B, by looking at the two cases from the uncertainty principle
Case 1: The stick is at an angle but not moving
At t = 0, θ = Δθ
θ = Δθ = A + B
At t = 0,
, A=B
This implies Δθ = 2A and we can then find
So we can now write
or
Case 2: The stick is at upright but moving
At t = 0, θ = 0
This condition gives us A = −B.
At t = 0,
This initial condition has come from the relationship between the tangential velocity, Δv which equals the distance to the centre of mass from the pivot point, and the angular velocity . Using the above initial condition gives us where
We can now write
[Award 4 marks for finding the two expressions for θ by using the two cases of the uncertainty principle.]
Now there are a few ways we can finish off this problem, we shall look at three different ways. In each case when the stick has fallen on the ground .
Method 1
Take and , use then rearrange for tf in both cases. We have
Look at the expression for cosh−1 x and sinh−1 x given in the question. They are almost identical, we can then approximate the two arguments to each other and we find,
we can then substitute in the uncertainty principle as and then write an expression of , which we can put back into our arccosh expression (or do it for Δv and put into arcsinh).
where and .
Method 2
In this next method, when you get to the inverse hyperbolic functions, you can take an expansion of their natural log forms in the tending to infinity limit. To first order both functions give ln 2x, we can then equate the arguments and find Δx or Δv in terms of the other and use the uncertainty principle. This would give the time taken as,
where and .
Method 3
Rather than using hyperbolic functions, you could do something like above and do an expansion of the exponentials in the two expressions for tf or we could make life even easier and do the following.
Disregard the e−ωt terms as they will be much smaller than the eωt terms. Equate the two expressions for and then take the natural logs, once again arriving at an expression of
where and .
This method efficiently sets B = 0 when applying the initial conditions.
[Award 2 marks for reaching an expression for t using one of the methods above or a suitable alternative that gives the correct units for time.]
Then, by using one of the expressions above for time, substitute in the values and find that t = 10.58 seconds.
[Award 1 mark for finding the correct time value of t = 10.58 seconds.]
- If you’re a student who wants to sign up for the 2025 edition of PLANCKS UK and Ireland, entries are now open at plancks.uk
The post PLANCKS physics quiz – the solutions appeared first on Physics World.